| 1. |
____________ is the ability to impress intelligence upon a transmission medium, such as radio waves. |
|
|
Modulation |
|
|
Medium |
| 2. |
The rate at which the vector rotates determines the FREQUENCY of the sine wave that is generated; that is, the faster the vector rotates, the more cycles completed in a given time period. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 3. |
The process of combining two or more frequencies in non-linear impedance results in the production of new frequencies. This process is referred to as______________. |
|
|
Heterodyning |
|
|
Demodulation |
| 4. |
Two conditions must be met in a circuit for heterodyning to occur. First, at least two different frequencies must be applied to the circuit. Second, these signals must be applied to non-linear impedance. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 5. |
Amplitude modulation refers to any method of varying the amplitude of an electromagnetic carrier frequency in accordance with the intelligence to be transmitted by the carrier. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 6. |
The “on-off” KEYING of a ______________carrier frequency was the principal method of modulating a carrier in the early days of electrical communications. |
|
|
Continuous wave |
|
|
Development |
| 7. |
When greater frequency stability is required, the oscillator should be keyed, but should remain in continuous operation; other transmitter circuits may be keyed |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 8. |
The categories of cw transmitters are as follows: |
|
|
Master oscillator power amplifier (mopa) transmitters, |
|
|
Multistage, high-power transmitters,
|
|
|
High- and very-high frequency transmitters |
|
|
All of the above |
| 9. |
The main advantage of a mopa transmitter is that the power-amplifier stage isolates the oscillator from the antenna. This prevents changes in antenna-to-ground capacitance from affecting the oscillator frequency. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 10. |
A______________ is an energy converter that changes sound energy into electrical energy. |
|
|
Microphone |
|
|
Diaphragm |
| 11. |
The sensitivity or efficiency of a microphone is usually expressed in terms of the electrical power level, which the microphone delivers to a matched-impedance load compared to the sound level being converted. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 12. |
An AM transmitter can be divided into major sections according to the frequencies at which they operate: |
|
|
Radio frequency (rf) unit |
|
|
Audio frequency (af) unit |
|
|
a & b |
|
|
None of the above |
| 13. |
What does FCC stand for? |
|
|
Federal Communications Commission |
|
|
Federal Communication Council |
|
|
Federal Communications and Connections |
|
|
None of the above |
| 14. |
To measure degrees of modulation less than 100 percent, you can use a MODULATION FACTOR (M) to indicate the relative magnitudes of the rf carrier and the audio-modulating signal. Numerically, the modulation factor is:
(Refer Pg 1-48) |
|
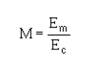 |
|
What does Em stand for in the above equation? |
|
|
RMS value of the modulation voltage |
|
|
Amplitude |
|
|
Frequency |
|
|
None of the above |
| 15. |
Plate modulation permits the transmitter to operate with high efficiency. It is the simplest of the modulators available and is also the easiest to adjust for proper operation. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 16. |
_______________ is modulation produced in the plate circuit of the last radio stage of the system. |
|
|
High-Level Modulation |
|
|
Low-Level Modulation |
| 17. |
The modulation index as a formula is shown below: |
|
 |
| What does ∆f stand for? |
|
|
Frequency deviation |
|
|
Modulation frequency |
|
|
Modulation factor |
|
|
None of the above |
| 18. |
In frequency modulation (fm) the instantaneous frequency of the radio frequency wave is varied in accordance with the modulating signal; the amplitude of the radio-frequency wave is kept constant. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 19. |
_____________________ is modulation in which we allow oscillations to occur for a given period of time only during selected intervals. |
|
|
Pulse modulation |
|
|
Phase Shift Keying |
| 20. |
Pulse Code Modulation is a method of pulse modulation in which the modulating wave is used to frequency modulate a pulse-generating circuit. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
|