| 1. |
Removal of material due to entrained sediment, ice, or debris rubbing against the boundary is defined as: |
|
|
Aggradation |
|
|
Abrasion |
|
|
Apron |
|
|
Material excavation |
| 2. |
Velocity at a given cross section determined by dividing discharge by: |
|
|
Time |
|
|
Speed |
|
|
Cross sectional area |
|
|
Viscosity |
| 3. |
Full flow in a culvert barrel is rare. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 4. |
Anchorage of the ends of long span culverts is required to prevent flotation or damage due to high velocities at the: |
|
|
Top |
|
|
Bottom |
|
|
Inlet |
|
|
Outlet |
| 5. |
The hydraulic condition in a culvert flowing full is called: |
|
|
Viscosity |
|
|
Hydraulic status |
|
|
Inflow |
|
|
Pressure flow |
| 6. |
If the cross-sectional area of the culvert in pressure flow were increased, the flow area would: |
|
|
Shrink |
|
|
Expand |
| 7. |
Free surface flow or open channel flow may be categorized as: |
|
|
Subcritical |
|
|
Critical |
|
|
Supercritical |
|
|
All of the above |
| 8. |
_____________ is required to force flow through a culvert. |
|
|
Heat |
|
|
Pressure |
|
|
Energy |
|
|
Force |
| 9. |
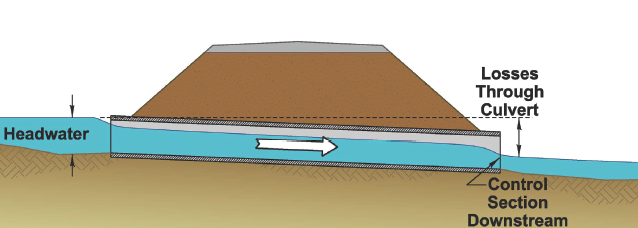
The picture above is: |
|
|
Submerged |
|
|
Unsubmerged |
| 10. |
Tailwater is the depth of water downstream of the culvert measured from the outlet invert. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 11. |
Since a culvert often constricts the available channel area, flow velocities in the culvert may be ________ than in the channel. |
|
|
Lower |
|
|
Higher |
| 12. |
A performance curve is a plot of headwater depth or elevation versus: |
|
|
Time |
|
|
Viscosity |
|
|
Flow rate |
|
|
Strain |
| 13. |
The hydraulic design of a culvert installation requires the evaluation of a large amount of data, such as: |
|
|
culvert location |
|
|
waterway data |
|
|
roadway data |
|
|
All of the above |
| 14. |
Stream cross sectional data acquired from a field survey at the site are highly desirable to supplement available topographic mapping. Ideally, a minimum of _________ cross sections should be taken, one upstream and one downstream. |
|
|
One |
|
|
Two |
|
|
Three |
|
|
Ten |
| 15. |
The allowable headwater is the maximum possible headwater, or ponding depth, at which side of the culvert? |
|
|
Upstream |
|
|
Downstream |
| 16. |
A slip liner is essentially a smaller-size conduit that is slipped inside a host pipe with the annulus between the two conduits typically grouted. The pipe used for slip lining may be a continuous length, or may be segmental. Slip lining is common in: |
|
|
Oval pipes |
|
|
Round pipes |
|
|
Symmetrical pipes |
|
|
Square pipes |
| 17. |
In outlet control, the hydraulic resistance of the culvert barrel must be calculated using a __________ loss equation. |
|
|
Friction |
|
|
Head |
|
|
Pressure |
|
|
None of the above |
| 18. |
The hydraulic radius is the cross-sectional area of a stream divided by: |
|
|
The pressure |
|
|
The wetted perimeter |
|
|
The flow |
|
|
The depth |
| 19. |
That portion of a streambank having an elevation less than the mean water level of the stream is the: |
|
|
Non alluvial channel |
|
|
Meandering stream |
|
|
Lower bank |
|
|
Upper bank |
| 20. |
Force or drag developed at the channel bed by flowing water is the: |
|
|
Unit shear force |
|
|
Unit strain |
|
|
Velocity |
|
|
Channel head |
|