| 1. |
Strength gain in concrete is a time-temperature dependent phenomenon commonly called ________.? |
|
|
Stiffness |
|
|
Maturity |
|
|
Porosity |
| 2. |
Which of the following is a type of curing compounds? |
|
|
Resin-solvent based |
|
|
Chlorinated-rubber based |
|
|
Wax-water based |
|
|
All the above |
| 3. |
________________ is defined in ACI 116R(1) as "change in volume produced by continued hydration of cement, exclusive of effects of applied load and change in either thermal condition or moisture content." |
|
|
Autonomous volume change |
|
|
Autogenous volume change |
|
|
Automatic volume change |
| 4. |
Which of the following are recognized methods of curing? |
|
|
Covering with plastic films |
|
|
Placing wet coverings |
|
|
Applying curing compounds |
|
|
All the above |
| 5. |
USACE guidance is to allow no more than a _________ gradient between the surface and a depth of 50 mm into the concrete (CEGS 03300, paragraph 3.15.6). |
|
|
8 °C |
|
|
11 °C |
|
|
13 °C |
|
|
18 °C |
| 6. |
Ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV) is related to the modulus of elasticity of the concrete. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 7. |
The _____________ is the time between when concrete is placed and when final curing operations can be initiated. |
|
|
Initial curing period |
|
|
Final curing period |
|
|
Intermediate curing period |
| 8. |
The rate of evaporation of bleed water is commonly estimated using the ____________.? |
|
|
ACI 290 nomograph |
|
|
ACI 301 nomograph |
|
|
ACI 303 nomograph |
|
|
ACI 308 nomograph |
| 9. |
Which of the following is not an ASTM recognized category? |
|
|
Type I |
|
|
Type II |
|
|
Type I/II |
|
|
Type V |
| 10. |
Portland-pozzolan mixtures hydrate __________ pure portland cement, and setting times are often extended. |
|
|
Slower than |
|
|
Same as |
|
|
Faster than |
| 11. |
Concretes with water-cement ratios less than ___________ are known to desiccate internally due to consumption of water during hydration. |
|
|
0.10 |
|
|
0.20 |
|
|
0.30 |
|
|
0.40 |
| 12. |
In the following equation for Estimated evaporation, what does V represent? where
ER is the estimated evaporation rate (lb/ft2/h),
eo is the vapor pressure of water at the evaporating surface (psi),
ea is the vapor pressure of water is air (psi)
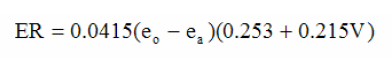 |
|
|
Volume |
|
|
Velocity |
|
|
Vapor |
| 13. |
In the following equation what is K?
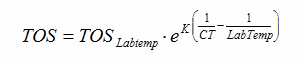 |
|
|
Kelvin |
|
|
Spring constant |
|
|
Activation energy |
|
|
Residual heat |
| 14. |
Paving mixtures are typically proportioned with relatively _________ cement contents and relatively low water-cement ratios. |
|
|
Low |
|
|
High |
| 15. |
Which of the following is not a test method for determining efficiency of curing of the near surface zone.? |
|
|
Rebound Hammer |
|
|
Water Absorption |
|
|
Solvent repulsion |
|
|
Abrasion resistance |
| 16. |
_______________ designed and built a relatively sophisticated test apparatus for measuring shrinkage of fresh concrete and related that property to water losses. |
|
|
Holt (2000) |
|
|
Bjontegaard, O. |
|
|
Stewart, Mark G. |
|
|
Gowripalan, N. |
| 17. |
Whether a curing compound application retains sufficient water under a given set of climatic conditions is strongly affected by which of the following properties.? |
|
|
Impermeability of the material |
|
|
Amount of application |
|
|
Temperature |
|
|
Both A & B |
| 18. |
Losses of too much water during the final curing period have been shown to negatively impact the quality of the near-surface zone of the concrete, as measured by water absorption and rebound number. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 19. |
In ________________ technique, a thermocouple in the concrete structure feeds back to a temperature controller on a curing chamber containing standard strength cylinders. |
|
|
temperature-matched curing |
|
|
thermocouple curing |
|
|
precast temperature curing |
| 20. |
Surface water absorption is a useful tool for measuring the quality of concrete curing. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
|