| 1. |
On October 19, 2021, at approximately 1:30 p.m., wood roof trusses collapsed and fell onto the ground floor at 1550 South Volusia Avenue, Orange City, Florida, where a Dollar General store was under construction (see Figure 1). Due to the collapse, two employees were injured after falling approximately 12 feet. A third employee cutting lumber on the ground floor inside the building, was fatally crushed by the falling trusses.
A structural engineer from the Office of Engineering Services (OES) in DOC reviewed the construction documents and supporting calculations and conducted an independent analysis to determine the cause of the collapse. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 2. |
The construction project consisted of constructing a ________________________ 70 feet wide and 130 feet long (see Figure 2). The ground floor was a 6-inch-thick concrete slab on grade. The framing walls (bearing walls) on four sides consisted of 2×6 lumber studs at 16 inches on center with double 2×6 top plates (see Figure 3). All framing walls were supported on a 2×6 bottom plate over 2-feet-wide continuous concrete footing. The north and south framing walls supported the roof trusses. The roof framing consisted of 66 wood piggyback base trusses spanning 70 feet in the north-south direction and spaced at 2 feet on center in the east-west direction (see Figure 4). The trusses were called piggyback because a piggyback base truss was used to support another smaller truss (piggyback truss) on its top chord at its north and south end. The framing walls on four sides and all piggyback base trusses had been constructed prior to the collapse. The smaller trusses were not installed at the time of the incident (see Figures 4 and 5). |
|
|
One-story commercial building |
|
|
Two story commercial building and office space. |
| 3. |
Three Top Rank employees were correcting bent roof trusses when the collapse occurred. The two surviving employees were eyewitnesses to the collapse and had pertinent information related to the investigation. |
|
|
Bent roof trusses |
|
|
The roof truss braces |
| 4. |
On the day of the incident, the three employees started work on the twisted roof trusses a little after 11:30 a.m. |
|
|
Twisted roof trusses |
|
|
broken roof trusses |
| 5. |
Around 1:30 p.m., the employee standing on the south wall heard a crack noise and observed the roof trusses move a little bit and were leaning toward __________________________________. He then observed the trusses starting to fall toward the inside of the building. |
|
|
The inside from where he was standing |
|
|
The outside from where he was standing |
| 6. |
In Fig. 12; Top Rank installed both diagonal and lateral braces (short lumber pieces) on the north and the south side of the trusses. Figure 12 shows the truss bracing installed on Nov. 4, 2021, after completion of piggyback base truss erection. Long diagonal and short member temporary lateral restraints installed on the north side of the trusses prior to the collapse. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 7. |
During the investigation it was discovered that bottom chord and web member bracing were not installed prior to the collapse (see Figure 14). |
|
|
Were installed |
|
|
Were not installed |
| 8. |
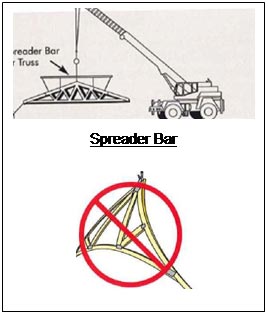
After reviewing the construction progress photographs taken by WW Build, OSHA found that the wood trusses were not properly hoisted. The erector did not follow the Building Component Safety Information Guide 1 to Good Practice for Handling, Installing, Restraining, and Bracing of Metal Plate Connected Wood Trusses, by using a spreader bar to hoist the trusses since they were over 60 feet long (see Attachment A). Wood trusses were found twisted and bent (or buckled) (see Figure 15). The mid-panel splice at the bottom chord of the west-most truss was damaged due to out-of-plane buckling during hoisting (see Figure 16).
|
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 9. |
Which one of the following was discovered during the analysis of the case.
- A 1 Roof Trusses properly designed the roof trusses (Piggy back base truss of 1 ply) for the prescribed loadings shown on the truss document.
- During the erection, only the top chord of each piggy back base truss was laterally braced, and the top chords were braced at approximately 8 locations only. Even without one employee standing on a truss, the truss was overstressed beyond its ultimate capacity under its own weight. Due to the lack of required lateral restraints, the installed trusses were unstable and ready to collapse due to out-of- plane buckling. The trusses were structurally inadequate for employees to use as an anchor for fall protection.
- The 70 feet long trusses were not properly hoisted. The trusses were prone to be overstressed during rigging due to out-of-plane buckling (i.e., twisting and bending), likely damaging the wood trusses and resulting in a nun safe condition.
|
|
|
1, and 2 |
|
|
1, and 3 |
|
|
1,2, and 3 |
| 10. |
Based on all analysis and investigation the conclusion was:
Based on the above, OES concluded that:
- The failure of the trusses occurred because of the out-of-plane buckling of the trusses due to inadequate bracings.
- The truss erector did not consult a professional engineer to design and determine the size and location of temporary bracings, as is required by industry practice if the truss span exceeds 60 feet. The span of the failed trusses was 70 feet.
- The temporary bracings provided by the erector were considered inadequate as per industry requirements, even for trusses having spans 60 feet or less.
- The load-bearing walls supporting the trusses at the site did not cause the collapse of the trusses.
- The trusses as erected were unstable and therefore structurally inadequate for employees to use as anchors for fall protection.
- Wind was not a causal factor.
|
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
|