| 1. |
Which is not a typical fresh water source for producing potable water? |
|
|
River |
|
|
Lake |
|
|
Deep groundwater |
|
|
Ocean |
| 2. |
Desalination processes remove _____________ from seawater and brackish water. |
|
|
Dissolved salts |
|
|
Minerals |
|
|
Dirt |
|
|
Oxygen |
| 3. |
The molecular weight cut off for RO membrane performance is typically in the range of __________ daltons for organic chemicals. |
|
|
50-100 |
|
|
100-300 |
|
|
300-500 |
|
|
Greater than 500 |
| 4. |
During pretreatment a disinfectant, often chlorine, will be added to ________ biofouling and protect the membrane from degradation. |
|
|
Increase |
|
|
Reduce |
| 5. |
Installation and operation of a desalination facility will have the potential for adverse impacts on air quality, water/sea environment, and ground water. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 6. |
The figure below shows the treatment plant process sequence of a typical plant.
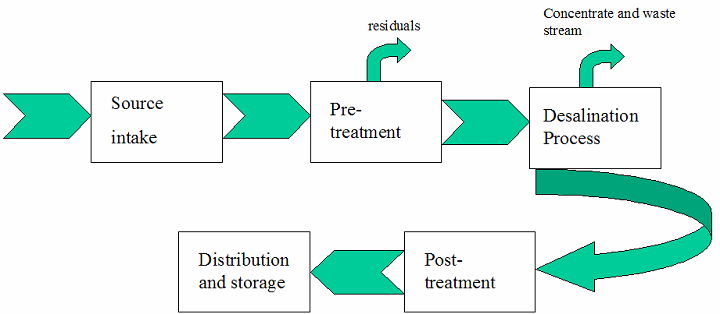
|
|
|
Post-Treatment |
|
|
Filtering |
|
|
Desalination |
|
|
None of the above |
| 7. |
_________________ subsurface intakes are more suitable for larger seawater desalination plants. |
|
|
Vertical |
|
|
Horizontal |
| 8. |
Open ocean intakes are suitable for all sizes of seawater desalination plants, but are typically more economical for plants of production capacity higher than ___________ . |
|
|
20,000 m³/day |
|
|
30,0000 m³/day |
|
|
40,000 m³/day |
|
|
50,000 m³/day |
| 9. |
The greatest single ecological impediment in selecting the site for a desalination facility is: |
|
|
Economic Impact |
|
|
Political Impact |
|
|
Environmental Impact |
|
|
None of the above |
| 10. |
Until the early 1990’s, __________ was the most commonly employed method of seawater desalination. |
|
|
Multistage flash distillation |
|
|
Thermal Desalination |
| 11. |
There is no direct contact between the heating steam system and the desalination process: |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 12. |
Membrane desalination is a process of separation of _____________ from the source water using semipermeable membranes. |
|
|
Oxygen |
|
|
Debris |
|
|
Minerals |
|
|
None of the above |
| 13. |
Salt rejection refers to the effectiveness of a membrane to ____________ salts from solution. |
|
|
Remove |
|
|
Add |
| 14. |
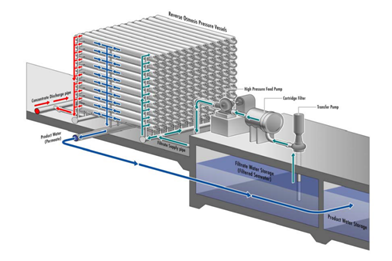
The figure above is an RO membrane with a _____________ pressure pump.
|
|
|
High |
|
|
Low |
| 15. |
_______________ is the most widely used disinfection method. |
|
|
Desalination |
|
|
Boiling |
|
|
Chlorination |
|
|
None of the above |
| 16. |
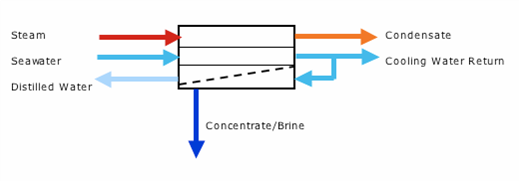
The figure above is of a ______________ unit.
|
|
|
Small distiller |
|
|
Vapour compression |
|
|
Desalination |
|
|
None of the above |
| 17. |
Pre-treatment of the source after intake water is normally designed to remove contaminants that will interfere with the __________ process such as by scale formation or fouling membranes. |
|
|
Disinfecting |
|
|
Post treatment |
|
|
Desalination |
|
|
Distilling |
| 18. |
The quality of the blended water is particularly relevant if mixing of incompletely treated water with desalinated water occurs __________ distribution. |
|
|
Prior to |
|
|
After |
| 19. |
Thermal processes generally require _________ pretreatment than membrane based processes. |
|
|
More |
|
|
Less |
| 20. |
General principles of post-treatment disinfection of desalinated water _______________ those of disinfection of freshwater sources of drinking water. |
|
|
are similar |
|
|
vary from |
| 21. |
Public health addresses: |
|
|
the quality of life |
|
|
improvement in community health |
|
|
potential risks associated directly or indirectly with the desalination project |
|
|
All of the above |
|