| 1. |
The size and configuration of the pumping station is determined by the sump area and depth required, the equipment clearances needed and, for larger plants, the need for other facilities such as interior maintenance space and personnel areas. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 2. |
Most pumping station facilities designed by the Corps of Engineers, whether operated by the Corps or a second party, should be designed for a functional life of 50 years. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 3. |
When determining the general plant layout and designing the features of a pumping station project, attention should be given to long term as well as first cost. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 4. |
Criteria for material selection, in descending order of importance, should be performance, durability, maintainability, economy, and aesthetics. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 5. |
Exterior building components should be selected, located, and installed in such a manner as to deter pilfering or physical damage to the station by vandals. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 6. |
All sheet and miscellaneous metal need not conform to applicable Federal Specifications, but should generally be of non-corroding material. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 7. |
For structures founded on soil, a determination of soil type, shear strength, cohesion, internal friction angle, and unit weights in dry, moist, and submerged conditions must be made for each material to be used in backfill or embankment sections and for each material in the foundation. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 8. |
If the foundation materials do not have sufficient bearing capacity to sustain the imposed structure loads, and if other stabilizing methods are impracticable or unfeasible, foundation piles may be required. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False
|
| 9. |
What does fig.4-1 illustrate about?
(Ref Pg.4-8) |
|
|
Typical structure uplift derivation |
|
|
Foundation plan |
|
|
Soil types |
|
|
None of the above |
| 10. |
What is the minimum uniformly distributed live load for roofs according to table 4-1? |
|
|
50 lb/sq ft |
|
|
35 lb/sq ft |
|
|
25 lb/sq ft |
|
|
15 lb/sq ft |
| 11. |
Operating floor must be designed to allow placement of the heaviest machinery piece anywhere on the floor unless specific areas are designated for this purpose. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 12. |
Roofs should generally be designed for dead load, live load, and either wind or seismic loading, which- ever is the more critical for the plant location. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 13. |
What does table 4-2 illustrate about?
(Ref Pg. 4-14) |
|
|
Stability criteria for pumping stations |
|
|
Operating loads |
|
|
Minimum live loads |
|
|
None of the above |
| 14. |
Joints between separate monoliths on large installations, and between the pumping station and adjacent wall sections when the pumping station is located on the protection line, are called construction joints. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 15. |
Water stops across contraction joints are necessary to prevent leakage and obtain dry operating and working conditions |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 16. |
A gravity drainage system may be constructed to carry normal runoffs through the protection line. It may be constructed separate from the pumping station or integral with it. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 17. |
The flotation safety factor SF, is defined as:
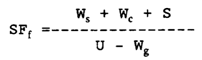
In the above equation what does S mean?
|
|
|
Surcharge loads |
|
|
Stability analysis factor |
|
|
Fluid load |
|
|
None of the above |
| 18. |
For normal operations, what is the minimum flotation safety factor SFf? |
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
1.2 |
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
1.5 |
| 19. |
What does figure B-1 illustrate about?
(Ref Pg. B-5)
|
|
|
Geometry and loading conditions |
|
|
Self weights |
|
|
Reinforced concrete loading diagram |
|
|
None of the above |
| 20. |
For stairways, what is the minimum live load (lb/sq ft) used in design? |
|
|
20 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
100 |
|
|
120 |
|