| 1. |
In this course, a pile foundation will be broadly described as one in which the following is true of the piles:
I. Piles are driven, not drilled.
II. Standard commercial, not special patent, piles are used.
III.Usually steel or prestressed concrete piles are used for major hydraulic structures, but reinforced concrete or timber piles should also be considered. |
|
|
I |
|
|
II&III |
|
|
I&III |
|
|
I&II&III |
| 2. |
What are the factors that have to be considered in the determination of pile type, length, spacing and batters? |
|
|
The nature of the structure. |
|
|
Type of applied loads. |
|
|
Technical and economic feasibility. |
|
|
All of the above. |
| 3. |
Structure or foundation failures can be categorized as an actual collapse or a functional failure. Functional failure can be due to excessive deflection, unacceptable differential movements, excessive vibration, and premature deterioration due to environmental factors. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 4. |
Factors of safety represent reserve capacity which a foundation or structure has against collapse for a given set of loads and design conditions. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 5. |
In determining the capacity of a pile foundation, it is important to consider the pile spacing along with the capacity of individual piles. The lateral load resistance of the piles may also be important since lateral loads can induce high bending stresses in a pile. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 6. |
The shear strength of the soil (s) can be calculated as:
(Refer: chap 3; pg 3-5)
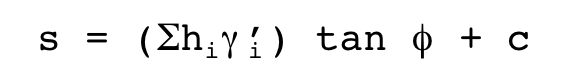
Where:
s=shear strength of the soil
hi= height of any stratum i overlying the point at which the strength is desired
Y i‘=effective unit weight in any stratum i above the point at which the strength is desired
Ø=?
c=cohesion intercept of the soil at the point at which the strength is desired
What does Ø mean? |
|
|
Minimum pile spacing |
|
|
Angle of internal friction of the soil at the point at which the strength is desired |
|
|
Lateral resistance of soil |
|
|
None of the above |
| 7. |
The axial capacity of a pile may be represented by the following formula:
(Refer: chap 4;pg 4-10)
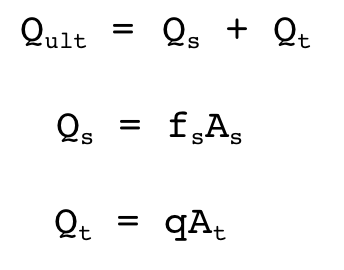
Where:
Qult = ultimate pile capacity
Qs = shaft resistance of the pile due to skin friction
Qt = tip resistance of the pile due to end bearing
fs = average unit skin resistance
As = surface area of the shaft in contact with the soil
q = unit tip-bearing capacity
At =?
In the above formula At denotes? |
|
|
Effective (gross) area of the tip of the pile in contact with the soil |
|
|
Average pressure |
|
|
Skin friction |
|
|
None of the above |
| 8. |
Negative skin friction is defined as the downward shear drag acting on piles due to downward movement of surrounding soil strata relative to the piles. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 9. |
Pile shoes are frequently used to improve driveability and also provide protection at the pile tip. When driving piles in dense sands, in hard layers containing cobbles or boulders, or through other obstructions, the shoe provides increased cutting ability and tip protection. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 10. |
Jetting is normally used when displacement-type piles are required to penetrate strata of dense, cohesion less soils. Exceptions are very coarse or loose gravel where experience shows jetting to be ineffective. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 11. |
Tension tests are often conducted on piles, which have previously been tested in axial compression. Some advantages to this are: a direct comparison of tension and compression on the same subsurface profile, cost savings in not having to drive an additional pile, and information on piles that must function in both tension and compression under operating conditions. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 12. |
Test piles should be loaded to failure when possible, as this test yields valuable information to the designer. Ideally, care must be taken as failure is approached to collect data more frequently than at sub-failure loads and to maintain the same rate of loading employed before reaching failure. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 13. |
A commonly used method to evaluate pile tests is one suggested by Davisson. The failure load is defined as the point at which the movement of the pile butt exceeds the elastic compression of the pile by 0.15 inch plus a factor (B/120) that is a function of pile diameter (B).
Which method is being explained above? |
|
|
Corps of Engineers Method |
|
|
Davisson Method |
| 14. |
The effects of driving many service piles may change the conditions existing during the test. Piles driven into a granular material may densify the foundation and increase pile capacity, while piles driven into a sensitive cohesive foundation may decrease pile capacity. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 15. |
The Contractor shall establish and maintain quality control for all operations to assure compliance with contract requirements and maintain records of his quality control for all construction operations, including but not limited to the following:
- Material
- Storing and handling
- Placing (location, alignment, etc.)
- Driving and splicing
- Cutting
|
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 16. |
Splicing of piling to make up the required lengths can be permitted. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 17. |
Steel H-piles stored at the job site shall be stored on a level surface in an area that will not pond water and the piles shall be stacked in such a manner that all piles have uniform support along their length without sagging or bending. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 18. |
Piles need not be accurately placed in the correct location and alignments, both laterally and longitudinally and to the vertical or batter lines as shown on the contract drawings. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 19. |
Piles can’t be driven within 100 feet of any concrete structure, unless and until a Contracting Officer authorizes it. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 20. |
To compute the average diameter of the tapered timber pile the following equation is used. (Refer D-4; pg 145)
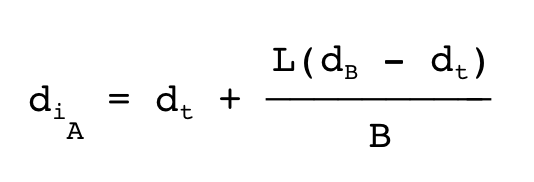
Where:
diA = diameter at the midpoint of the layer being computed
dt = ?
dB = diameter of pile butt
L = length from pile tip to midpoint of layer
B = total length of pile
What does dt mean in the above equation? |
|
|
Diameter of pile tip |
|
|
Density of the soil |
|